Having lived with Crohn’s disease for 43 years, and an ostomy for 35, Lori Plung had known it was possible she would go on to develop Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS). Eight years ago, following her fifth surgery, SBS and the need for intravenous nutrition (TPN) became a reality.
In recognition of Crohn’s and Colitis Awareness Week (1-7 December 2023), Lori generously shares some of her experiences, and the advice she’d give to anyone grappling with complexities of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) who may be facing the possibility of developing SBS as a result of surgical procedures to treat their disease.
Learning to live with Crohn’s and an ostomy
When I was diagnosed with Crohn’s disease at 16 years old, the thought of having to have “a bag” was, quite frankly, terrifying. But at the age of 24, the disease overtook my entire being. I had debilitating pain, cramps, bloody diarrhea and urgency, and I was up multiple times a night – I often couldn’t leave my house for fear of an accident. I was too sick to eat and had no energy.
Eventually I needed an emergency proctocolectomy. My colon, rectum, and terminal ileum were removed, and replaced with a permanent ileostomy. I had been so sick before surgery that I was very weak, and recovery was incredibly hard.
But what surprised me most? The feeling of relief. I was free! As I recovered from the procedure, my pain and symptoms were gone. Suddenly, I could eat what I wanted, and I started feeling back to myself. My quality of life improved and my stoma became my new best friend.
Though I was grateful for this new lease on life, it came with challenges. The Crohn’s disease returned a year later in my small bowel, presenting as multiple strictures and obstructions. I was now navigating flares with an ostomy, often experiencing high output which required supplemental outpatient intravenous hydration, magnesium, and potassium to get my levels back to normal.
What is Short Bowel Syndrome?
Five more surgeries followed in the span of 32 years, with the intention of saving as much bowel as possible. I heard mumbles of avoiding “short gut”, but nobody sat down and explained what that meant. I wish I’d known more about it sooner.
Short gut, also known as Short Bowel Syndrome (SBS), occurs when your bowel doesn’t have enough length to absorb the nutrition and hydration your body needs on its own. In most cases, it happens as a result of major surgical resection of the small intestine, necessitated by conditions like Crohn’s and colitis. For a patient like me, with only 69cm of intestine remaining, intravenous nutrition and hydration support is needed to keep my body functioning properly. This is known as Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN).
Coming to terms with a new normal
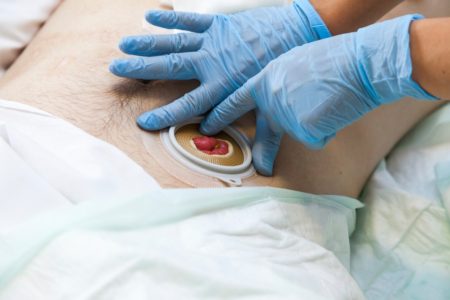
 TPN nourishes my body with the nutrients it’s not capable of absorbing on its own. It’s delivered via a Hickman catheter in the upper left part of my chest, infusing through a pump stored in a backpack while I sleep.
TPN nourishes my body with the nutrients it’s not capable of absorbing on its own. It’s delivered via a Hickman catheter in the upper left part of my chest, infusing through a pump stored in a backpack while I sleep.
Coming to terms with that wasn’t easy for me. I’d been on TPN before surgery to increase my nutritional status, and I assumed I would be off it at some point during my recovery. But with the SBS diagnosis, that was unlikely to happen. I had a very hard time accepting the fact that I would have to live with a central line for the rest of my life.
Therapy has been invaluable in helping me learn how to cope and accept. I learned that I can dislike having to hook into my TPN each night, and at the same time, I can be grateful for it, and for the life it allows me to lead. These two truths can co-exist together – and that way of thinking has helped me to accept my new normal.
Goals

I’m also hopeful that I can reduce my reliance on TPN over time. For patients like me, the goal of SBS management is to increase valuable time off TPN through intestinal rehabilitation. This uses approaches including diet, medications, and surgery to help the remaining GI tract work better so that it can absorb more nutrients from eating. Not all SBS patients are the same, so it’s important to understand each individual’s needs and explore the best options.
It’s also crucial to have the support of a medical team that specializes in IBD and intestinal rehab. Since my SBS diagnosis, I was careful to choose a multidisciplinary team at an academic medical center that is part of the Gastroenterology Rehabilitation and Transplant Program. My physician is an IBD specialist and the director of the nutrition support program, and I’ve worked closely with a dietitian who specializes in treating patients with SBS. Their support has been life-changing.
Need to Know
Having spent over 40 years navigating the complex journey from Crohn’s to SBS, I am now an advocate for patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Here are some of the most important things I think patients should know when managing their own condition:
- Preserving Bowel
As a Crohn’s patient, it’s important to be aware of potential complications of surgery, and the possibility that losing large sections of small bowel can lead to SBS. Make sure to discuss this with your healthcare team before surgery, and wherever possible, look for ways of minimizing bowel loss. - Learn About SBS
Being educated, and aware of the resources available to you, gives you the opportunity to have important discussions with your medical team and seek out the best possible care. You can access resources, support, and education through UOAA and other organizations such as the Oley Foundation, IFFGD, Transplant Unwrapped, The Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation, and The Short Bowel Syndrome Foundation - Find the Right Team
Seek out a medical team with expertise in SBS and nutrition to offer you the right support throughout your journey. Ideally, this should be at a center that offers intestinal rehabilitation with a multidisciplinary team. If this isn’t possible, find out if your medical team is willing to consult with such a center. - Nutrition Matters
Pay close attention to your diet. Some foods may lead to increased ostomy output or difficulties in digestion. Staying hydrated and making wise food choices are essential. Learn what works best for your specific condition and consult an ostomy nurse and an IBD/SBS dietitian for guidance. - Advocate for yourself
Being comfortable advocating for yourself does not mean being confrontational. It’s about being heard, understood, and well cared for without feeling dismissed. Open communication with your healthcare team is important, especially when shared decision-making comes into play. - Resilience
Day to day life with these diseases can be hard. Sometimes we have to take things day by day, hour by hour, and even minute by minute to get through the tough times. I believe that every patient is resilient. Sometimes, it’s buried, and we just need a bit of extra support to help it come to the surface. - Seek support
Actively engage with your IBD community. Bowel diseases are very private and isolating, so being surrounded by others who understand firsthand what you are experiencing is very powerful. Family and friends can be supportive, but they can only empathize. Speaking with actual patients who have “been there, done that” is extremely helpful and comforting! - Be kind to yourself.
Self-compassion and self-care are very important when living with the day-to-day challenges of these diseases. For example, fatigue is one of the biggest symptoms of IBD. Giving ourselves permission to rest can be hard for some of us – me included! That’s where self-care and self-compassion come in. - Be positive
Lastly, it is absolutely and positively possible to live a very happy and productive life while living with conditions like Crohn’s disease and SBS.
[Article written by Lori Plung with support from UOAA digital sponsor, VectivBio.]
VectivBio is a global biotechnology company committed to improving the lives of people with short bowel syndrome, who rely on parenteral support (IV nutrition and/or IV hydration). VectivBio is part of Ironwood Pharmaceuticals Inc., a leading global gastrointestinal (GI) healthcare company on a mission to advance the treatment of GI diseases and redefine the standard of care for GI patients. To learn more, visit VectivBio.com.







 pantyliners in my underwear. When I retired from active duty in August 1996, I immediately started my second career as an Army JROTC Instructor in Bennettsville SC. I continued to go to the bathroom quite frequently and in the spring of the following year my daughter, who was six at the time, wanted me to play horsey with her and take her around the block. I bent down half in tears and told her that “daddy can’t play horsey because he is too sore on his bottom”. I immediately went to talk to my wife and we both agreed it was time to get back to having an ostomy bag. That summer at the Columbia SC Veterans Administration hospital, I had my third surgery to restore my ostomy due to my poor quality of life with the J Pouch. On the positive side, since I’ve had an external pouch, the veteran’s administration awarded me 100% total and permanent disability. I spent the next 23 years as an Army JROTC Instructor.
pantyliners in my underwear. When I retired from active duty in August 1996, I immediately started my second career as an Army JROTC Instructor in Bennettsville SC. I continued to go to the bathroom quite frequently and in the spring of the following year my daughter, who was six at the time, wanted me to play horsey with her and take her around the block. I bent down half in tears and told her that “daddy can’t play horsey because he is too sore on his bottom”. I immediately went to talk to my wife and we both agreed it was time to get back to having an ostomy bag. That summer at the Columbia SC Veterans Administration hospital, I had my third surgery to restore my ostomy due to my poor quality of life with the J Pouch. On the positive side, since I’ve had an external pouch, the veteran’s administration awarded me 100% total and permanent disability. I spent the next 23 years as an Army JROTC Instructor.
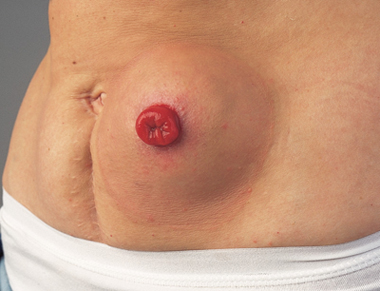 intestine and the weak spot is in the same area the surgeon created your stoma.
intestine and the weak spot is in the same area the surgeon created your stoma.



