A New Guide aims to help you find the right words to talk about your ostomy
By Joga Ivatury, M.D., MHA
The Speaking Stoma Guide is the first health communication guide for people with ostomies. This work was coproduced through collaboration with ostomates worldwide, UOAA, clinical experts, and health communication experts. This guide is freely available here on UOAA’s website, encompassing 11 communication topics areas including managing pouch leaks, communicating with friends and family, and intimacy.
experts, and health communication experts. This guide is freely available here on UOAA’s website, encompassing 11 communication topics areas including managing pouch leaks, communicating with friends and family, and intimacy.
This work has been inspired by our experience working with ostomates. We recognize that talking about your ostomy will not always be easy. We created the Speaking Stoma Guide to help. We hope this guide gives you an idea of things you could say if you are ever in similar situations and ways to manage challenging social situations that may arise. Each section has a big topic and has different situations that you may experience. In the next section, we will provide a snapshot of situations inspired by real people with ostomies.
Leaks
In this section, we have suggestions for what you might say to help manage the situation based on how much you want to disclose about having an ostomy. These phrases were produced directly from things ostomates told us. For people who did not want to disclose anything about having an ostomy (low disclosure), a person may say, “Can you show me how to get to the bathroom?” For high disclosure, a person may say, “Can you show me how to get to the restroom? My ostomy pouch has leaked and I need to clean up. Would you be able to find me an extra set of clothes? I really appreciate it!” Each section has several suggestions like this.
Talking About Food
With an ostomy, some people have limitations on the food that they can eat. Some ostomates expressed embarrassment when they couldn’t eat the same food everyone else is eating. It’s hard to say “no” whenever someone offers you food. One participant noted that he once told a host on behalf of his wife: “Please don’t take offense. She doesn’t eat these things. It’s not your cooking.” For higher disclosure, a person may say “Thank you so much for inviting me. After my surgery I’m still figuring out the foods that make me feel best, so I ate before I came. Everything looks delicious!” In general, there are many people with and without ostomies that have dietary restrictions.

Public Restrooms
What do you do when you need to use a public restroom to care for your ostomy and there is a long line! For low disclosure, you may consider saying: “Excuse me, I have an emergency and need to get to a restroom right now.” This does not reveal anything to strangers except the urgent need. For higher disclosure, you may reveal the presence of your ostomy and the rapid need for its care. People in line can be helpful too. One of our participants recalls how a stranger helped her get to the front of the line during a pouch leak.

Talking to Friends and Family
Time with friends and family are vital to everyone. How do you address having an ostomy with them? Some of our participants suggested having a “code name” for the ostomy that they can use with their family and friends to talk it in public. Unfortunately, some people have disparaging comments or jokes about ostomies once they know about it. Some ostomates use humor back to deflect the situation. It is also ok to say: “I am not really comfortable joking about my ostomy like that, but I am glad you will be willing to help if I need it. I really appreciate it.”
Noises
Noises happen! People with ostomies have no control of when they happen. In the beginning, our participants noted that they felt awkward about the noises their ostomies made. It helped people to remember that no one knows that the noises came from the ostomy. It is ok to say nothing (low disclosure). It is also ok to say: “Excuse me, I have an ostomy pouch and sometimes it makes noises” (medium disclosure).
people to remember that no one knows that the noises came from the ostomy. It is ok to say nothing (low disclosure). It is also ok to say: “Excuse me, I have an ostomy pouch and sometimes it makes noises” (medium disclosure).
Sex and Intimacy
Some people are not sure when or how to tell a romantic partner about their ostomy. There is no right or wrong time. Some people may choose to tell someone immediately, while other people might wait to tell the person until they know the person better. Your comfort is what is most important. We have suggestions and real-life testimonies in the guide related to speaking about sex and intimacy while having an ostomy.
Talking to Clinicians
We also go through ways to manage different levels of challenging social situations or what we term as “difficulty.” For example, you are in a clinical visit with a new physician who is not familiar with ostomies. Our participants universally encountered this situation. They noted that they often are the most knowledgeable person about ostomies in a clinical visit. In the guide we provide some easy to remember suggestions about how to manage this situation and others.
What’s Next?
We are scientists and this work does not end here. We are actively working to obtain funding to test this guide to see if it makes a difference for people with ostomies. We have also translated the guide into Spanish and are pilot testing it with people who prefer to speak in Spanish. Our experiences with major grant organizations, however, has been underwhelming to say the least. Some reviewers talk about “osteotomies” (surgically created bone holes) instead of ostomies demonstrating their complete lack of basic understanding. Other reviewers assumed that existing information already contained a wealth of communication-related information for ostomates. Despite these, we are undeterred and will keep pushing forward for funding. We would appreciate any support for this work from anyone including the ostomy community, ostomy pouch manufacturers, and local/state health agencies to keep the momentum going! We would also appreciate your feedback on the Speaking Stoma Guide. Please feel free to email me at jivatury@austin.utexas.edu.
Joga Ivatury, M.D., MHA, is an associate professor of surgery Dell Medical School and the inaugural chief of colon and rectal surgery at UT Health Austin. The Speaking Stoma Project was funded through the Communication for Health, Empathy, and Resilience Grant Program and created in partnership with Dell Medical School and the Center for Health Communication at The University of Texas at Austin.
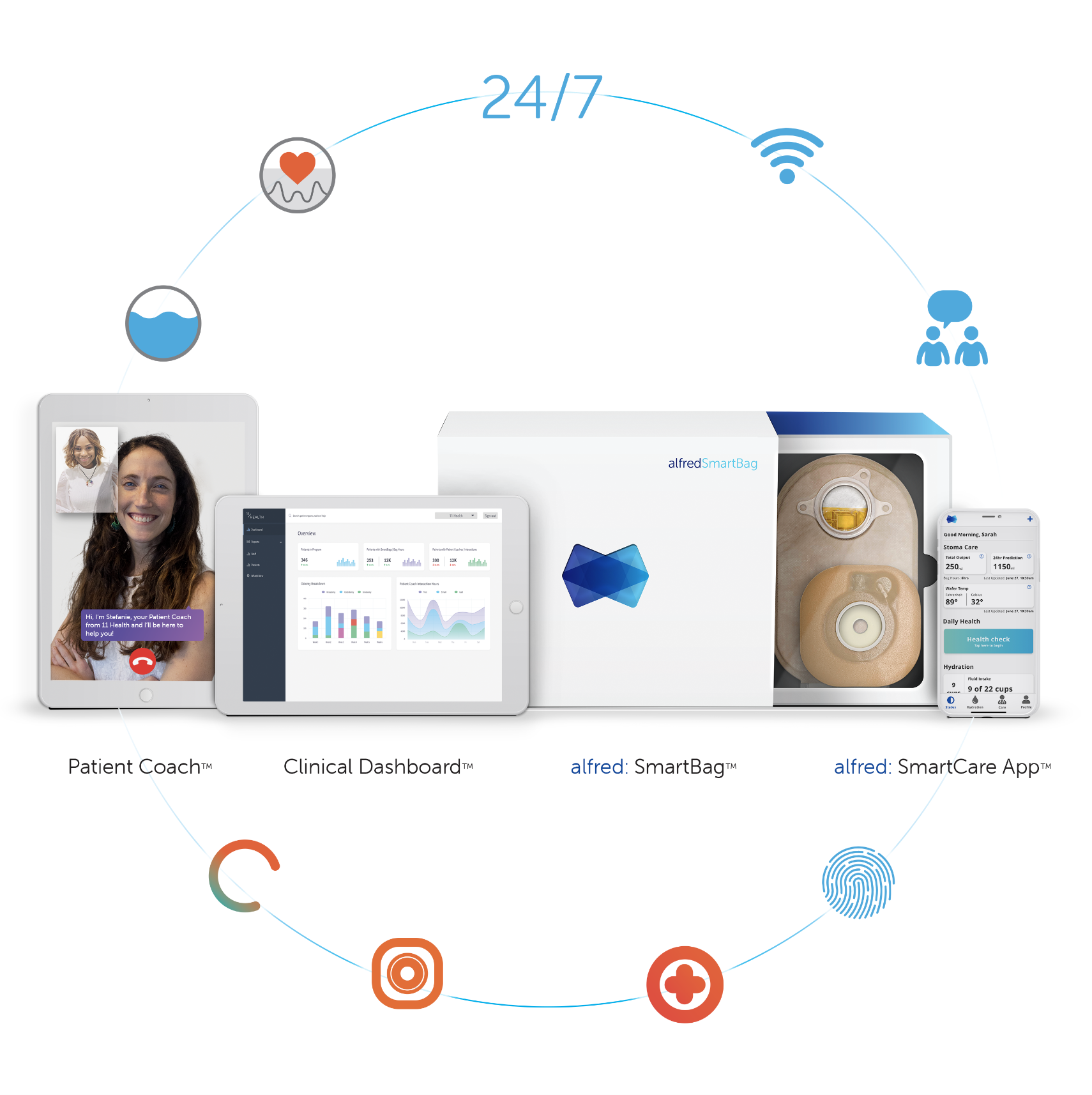
 being admitted within the first 90 days post operatively [1]. This is one of the highest rates of readmission when compared to other types of surgery. The most common cause for re-admission is dehydration, at approximately 40% of post ileostomy readmissions [2]. We also know that 84% of ostomy patients develop skin issues. The causes of these can be chemical, mechanical, or microbial, and possibly avoidable. Ostomates also have significantly increased healthcare costs, especially when affected by peristomal skin complications, and leakage [2]. It is known that 25% of ostomates develop renal failure within two years. The complications these patients encounter require 7x more outpatient visits than the average patient. And 29.1% of ostomates experience readmission which costs approximately $16,000 per patient [1]. These statistics show that specialized care for these patients is imperative to improving patient outcomes in this patient population.
being admitted within the first 90 days post operatively [1]. This is one of the highest rates of readmission when compared to other types of surgery. The most common cause for re-admission is dehydration, at approximately 40% of post ileostomy readmissions [2]. We also know that 84% of ostomy patients develop skin issues. The causes of these can be chemical, mechanical, or microbial, and possibly avoidable. Ostomates also have significantly increased healthcare costs, especially when affected by peristomal skin complications, and leakage [2]. It is known that 25% of ostomates develop renal failure within two years. The complications these patients encounter require 7x more outpatient visits than the average patient. And 29.1% of ostomates experience readmission which costs approximately $16,000 per patient [1]. These statistics show that specialized care for these patients is imperative to improving patient outcomes in this patient population.

