A patient who did not know what to expect walks you through the process (with photos)
By AnneMarie Finn
According to UOAA information on this website, a urostomy is “a surgically created opening in the abdominal wall through which urine passes. A urostomy may be performed when the bladder is either not functioning or has to be removed. There are several different types of surgeries, but the most common are ileal conduit and colonic conduit. Reasons for surgery include bladder cancer, spinal cord injuries, malfunction such as chronic infection of the bladder and birth defects such as spina bifida.” Great definition, but what does it mean? When I was told I would need a radical cystectomy, leading to an ileal conduit I had no clue. The following is my experience.
Because of bladder cancer, my bladder needed to be removed and a new way to pass urine created. Due to the location of the tumor, my urethra was also removed so my surgeon and I settled on an ileal conduit, a conventional urostomy. It is called ileal conduit because a piece of the ileum, or small bowel, is used to make a passage for urine to go from the kidneys and ureters out of the body. The other end is brought out through a hole in the abdomen where urine exits through a stoma (more on that shortly). It is known as an incontinent urinary diversion because you cannot control the urine. As a result, a collection bag or pouch hangs from your abdomen to catch the urine. The pouch is not visible as it is worn under your clothes. Still not clear? It wasn’t for me either.

A couple of days before surgery, I met with an ostomy nurse at the hospital where I would be receiving my surgery. She marked where the stoma would be placed. She saw how I wore my pants. She had me sit, stand, lay down, and bend over, She drew a mark with a marker about 2.5 inches to the right and 3 inches down from my navel and covered it with a waterproof dressing. This would guide the surgeon as to the optimal spot to place the stoma. The surgeon had the ultimate call on where the stoma went, depending on the surgery itself. I also met with a nurse for a pre-op appointment. They went through the typical exam and then explained the ERAS protocol to me. ERAS, Enhanced Recovery After Surgery, is used at my hospital for radical cystectomies. They no longer use a bowel prep. You drink a high carbohydrate drink in the hours prior to your surgery. They get you up walking and feed you by the day after surgery. The goal is to keep your bowels working. This reduces the length of hospital stay and the number of complications.
This is major surgery. It is considered one of the most complex cancer surgeries performed. My surgery took 7 hours. They removed the bladder, urethra, uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, an ovary, and some lymph nodes. When I woke up, I had a bag, a large incision with more than 30 staples and a Jackson Pratt (JP) drain on my abdomen. I also had intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) devices on my legs, my spa legs. Blood clots are a common side effect of a radical cystectomy. Because of that, I also received daily prophylaxis blood thinner shots in my belly for 30 days.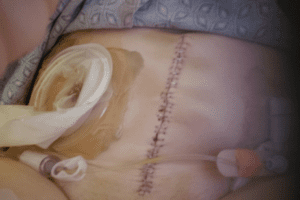 I was not in a great deal of pain which was easily managed with Tylenol. I was definitely weak, but otherwise ok. I went home in 4 days, on my own with my urostomy.
I was not in a great deal of pain which was easily managed with Tylenol. I was definitely weak, but otherwise ok. I went home in 4 days, on my own with my urostomy.
The stoma is the badge of the urostomy. My stoma is about one inch in diameter. It is pretty round, It sticks out. It sometimes moves in and out. You can’t feel it. It has been described as looking like a rosebud. It is red. This is where the urine exits the body. You have no control over it. Sometimes it will also expel mucus. Some people name them. I did.
 Rudolph, my red, round stoma
Rudolph, my red, round stoma
You use a urine collection pouch, or bag, to catch the urine. The hospital will send you home with some so you do not need to have them on hand before you get home. There are many different brands. In fact, until I found what worked best for me, I tried most of them. My pouch is about 8 inches long, 6-7 inches wide and has a 1-2 inch closable spout on the bottom. It also is a deep convex bag as my stoma does not stick out very far and it helps protect my skin. I prefer the clear bag so I can see the stoma and center it when I put it on. There are both one and two-piece bags. I have used both. One-piece pouches have the bag and a skin barrier attached. The skin barrier has adhesive, also called a flange or wafer, that sticks to your skin. There is a hole that goes over the stoma. Some are pre-cut, some are not. If not, you must cut a hole slightly bigger than your stoma before putting it on. There are also two-piece systems. The bags are separate from the skin barrier. They are attached by a Tupperware-like seal. You can leave the skin barrier on and take off the pouch.

Front and back of 1 piece, deep convex pouch
I change my pouch every 3 days. I like to remove the old pouch and take a shower with it off. I feel so free. To remove, I use an adhesive removal spray and wipes to clean the skin. I shower and wash the area around the stoma with soap and dandruff shampoo, which contains Zinc. Some people wash with a vinegar and water combo. If I change without showering, I just use plain water to rinse. After showering, I use a hairdryer on the lowest setting to dry the skin around the stoma so the wafer sticks to it. Drying your skin is important. I have some skin issues so I also use a skin barrier protective sheet, that I cut a hole to match the opening of the wafer, and a cohesive seal.
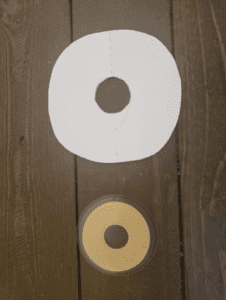
Protective Sheet with hole cut out and Cohesive Seal
Some people use powders, paste, barrier wipes, etc. I do not. It took a lot of trial and error to find what worked best for me. You need to find what works for you. One of the best ways to do this is to work with an ostomy nurse. They can help you navigate ordering and finding the best system for you.
At night, I use the urinary drainage bag they sent me home with from the hospital. For me, it works the best. There are several brands of night bags and even jugs. I put it on the floor next to my bed inside of a small wastebasket. This has been key as the drain has opened (or been left open) and the wastebasket collected the urine, preventing a rug catastrophe. I am a very active sleeper and I am not really hindered too much from my bag. I am able to sleep on my back, sides, and stomach. Don’t be afraid to sleep. People add their own tubing and tube placement strategies. Use whatever works for you. I also highly recommend a waterproof mattress pad. Mattresses are expensive. I also use the night drainage bag on long car trips. I don’t have to stop and use those disgusting public toilets. I even used it during the Avengers finale. I was probably the only person in the theater who did not have to get up to use the facilities during the movie! People were actually jealous.
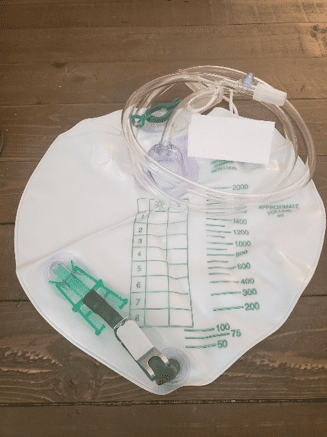 Night Drainage Pouch
Night Drainage Pouch
I honestly can’t even feel my pouch. I empty it every 1-2 hours, depending on how much I drink. Sometimes there is a “ghost” feeling where my bladder used to be making it feel like I have to pee. Ah, the good old days. It is actually a weird sensation drinking a lot and not feeling like I have to go. The bag is not noticeable under my clothes. I really do wear what I wore before surgery: jeans, sheath dresses, shorts, and bathing suits. I am still sexually active. Having gone through this experience with my wonderful caregiver, my husband, has brought us closer. Most importantly, I am cancer-free.



 Wow. Right?
Wow. Right?
