Colostomy and Ileostomy Pouches
Can be either open-ended, requiring a closing device (traditionally a clamp or tail clip); or closed and sealed at the bottom. Open-ended pouches are called drainable and are left attached to the body while emptying. Closed end pouches are most commonly used by colostomates who can irrigate (see below) or by patients who have regular elimination patterns. Closed end pouches are usually discarded after one use.
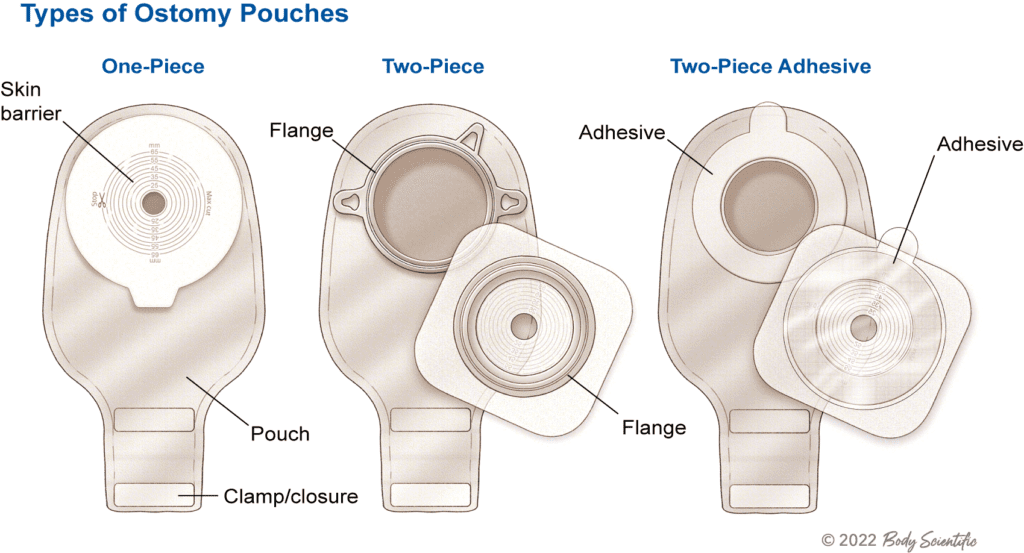
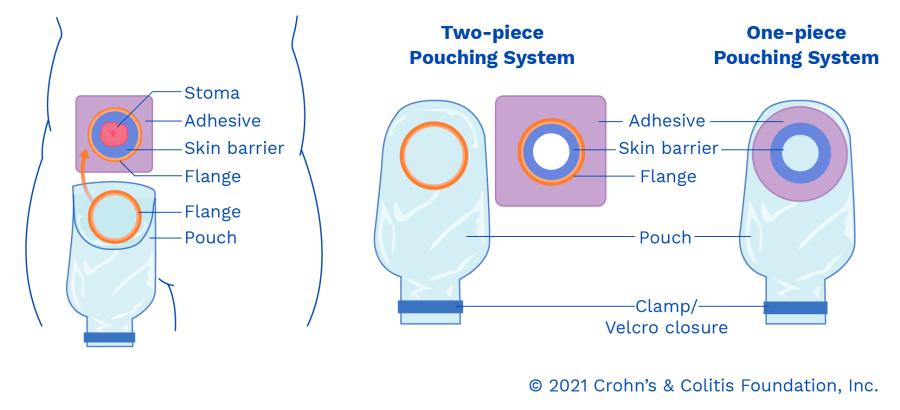
Two-Piece Systems
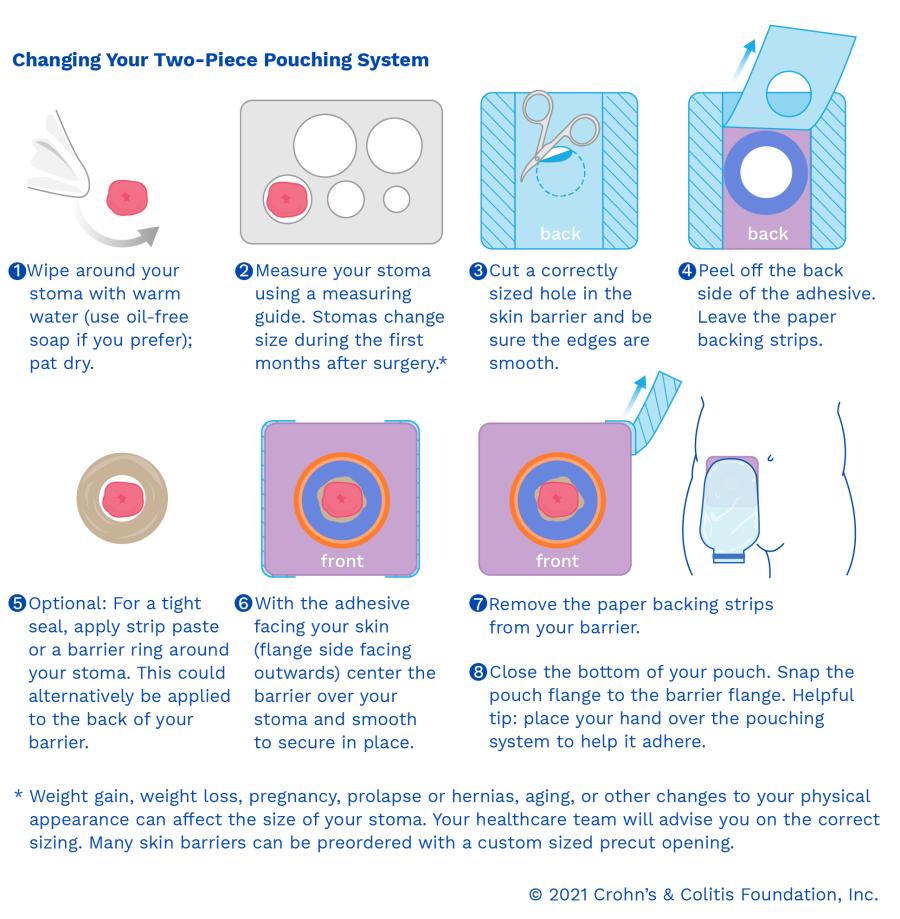
Allow changing pouches while leaving the barrier/wafer attached to the skin. The wafer/barrier is part of a “flange” unit. The pouches include a closing ring that attaches mechanically to a mating piece on the flange. A common connection mechanism consists of a pressure fit snap ring, similar to that used in Tupperware™.
One-Piece Systems
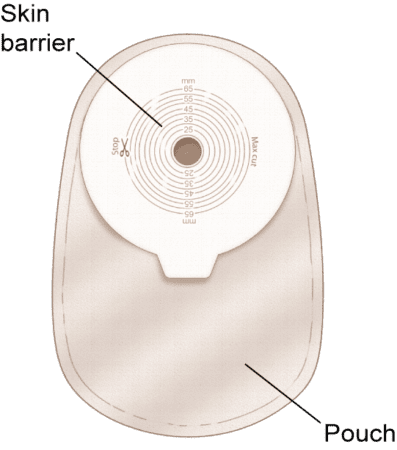
Colostomy Pouch One-Piece Closed End
Consist of a skin barrier/wafer and pouch joined together as a single unit. Provide greater simplicity than two-piece systems but require changing the entire unit, including skin barrier, when the pouch is changed.
Consist of a skin barrier/wafer and pouch joined together as a single unit. Provide greater simplicity than two-piece systems but require changing the entire unit, including skin barrier, when the pouch is changed.
Both one-piece and two-piece pouches may be either drainable or closed.
Irrigation Systems
Some colostomates can “irrigate,” using a procedure analogous to an enema. This is done to clean stool directly out of the colon through the stoma. This requires a special irrigation system, consisting of an irrigation bag with a connecting tube (or catheter), a stoma cone and an irrigation sleeve. A special lubricant is sometimes used on the stoma in preparation for irrigation. Following irrigation, some colostomates can use a stoma cap, a one- or two-piece system which simply covers and protects the stoma. This procedure is usually done to avoid the need to wear a pouch.
Urinary Pouching Systems
Urostomates can use either one or two-piece systems. However, these systems also contain a special valve or spout which adapts to either a leg bag or to a night drain tube connecting to a special drainable bag or bottle.
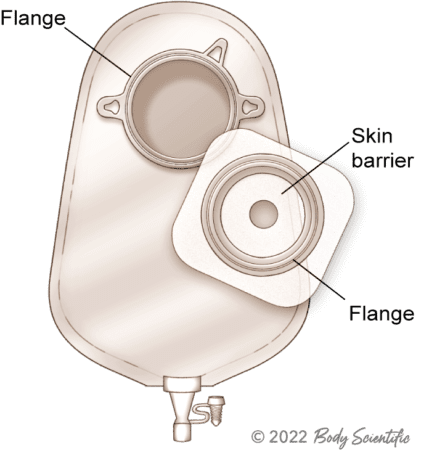
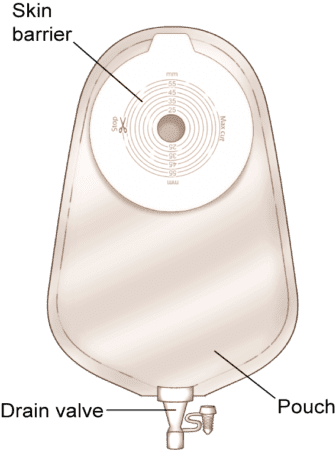
Styles of Pouching Systems
The items above are the major types of pouching systems. There are also a number of styles. The skin barriers/wafers in both one-piece and two-piece systems may be either flat or convex (curved to press inward on skin adjacent to the stoma). Skin barriers may be made of either standard-wear or extended-wear materials. Some barriers are fairly rigid and some very flexible. There are barriers with and without adhesive backing and with and without a perimeter of tape. Stoma openings may be either pre-cut or cut-to-fit. Some manufacturers have introduced drainable pouches with a built-in tail closure that doesn’t require a separate clip. The decision as to what particular type of system to choose is a personal one geared to each individual’s needs. There is no right or wrong choice, but each person must find the system that performs best for him or her.
The larger mail-order catalogues will illustrate the types and styles from all or most of the suppliers. If you have any trouble with your current pouching system, discuss the problem with an ostomy nurse or other caregiver and find a system that works better for you. It is not uncommon to try several types until the best solution is found. Free samples are readily available for you to try. There is no reason to stay with a poorly performing or uncomfortable pouching system.
Types of Accessories
You may need or want to purchase certain pouching accessories. The most common items are listed below.
Convex Inserts
Convex shaped plastic discs that are inserted inside the flange of specific two-piece products. Some barrier rings and strips (see below) can also be used to add convexity to a pouching system.
Skin Barrier Pastes, Rings and Strips
These materials can be used to smooth out irregularities of the peristomal skin or otherwise fill in space between the stoma and peristomal skin and the pouching system’s wafer. This may reduce leaks and improve wear time. Note that ostomy “paste” is used as a caulking material; it is not an adhesive. In fact, using too much paste can reduce adherence of a pouching system.
Ostomy Belts
Belts that wrap around the abdomen and attach to the loops found on certain pouches. Belts can also be used to help support the pouch or as an alternative to adhesives if skin problems develop. A belt may be helpful in maintaining an adequate seal when using a convex skin barrier.
Pouch Covers
Made with a cotton or cotton blend backing, easily fit over the pouch and protect and comfort the skin. They are often used to cover the pouch during intimate occasions. Many pouches now include built-in cloth covers on one or both sides, reducing the need for separate pouch covers.
Skin Barrier Liquid/Wipes/Powder
These products can be most useful when peristomal skin is irritated, moist or weepy. Powders can help skin to heal (excess powder should be wiped off after applying). Irritated skin can also be sealed with a liquid film barrier (applied with wipes, sprays or liquids, then allowed to dry) before applying the pouching system.
Tapes
Tapes are sometimes used to help support the wafer or flange (faceplate) and for waterproofing. They are available in a wide range of materials to meet the needs of different skin sensitivities.
Adhesive Remover
Adhesive removers may be helpful in removing wafers or tapes, or cleaning the residues that may remain after removing such adhesives.
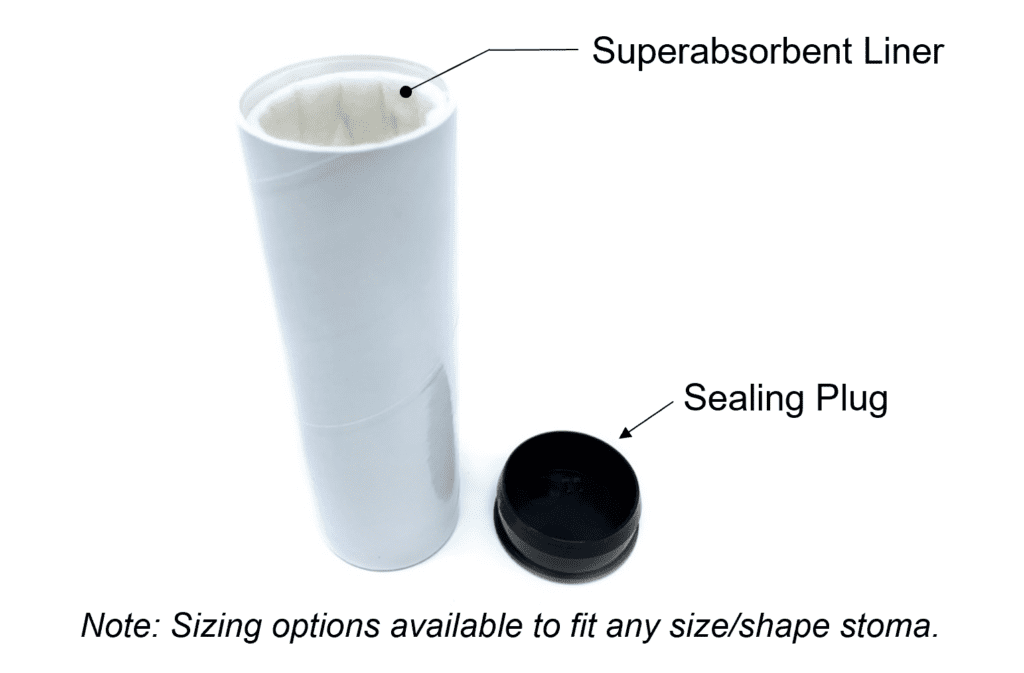
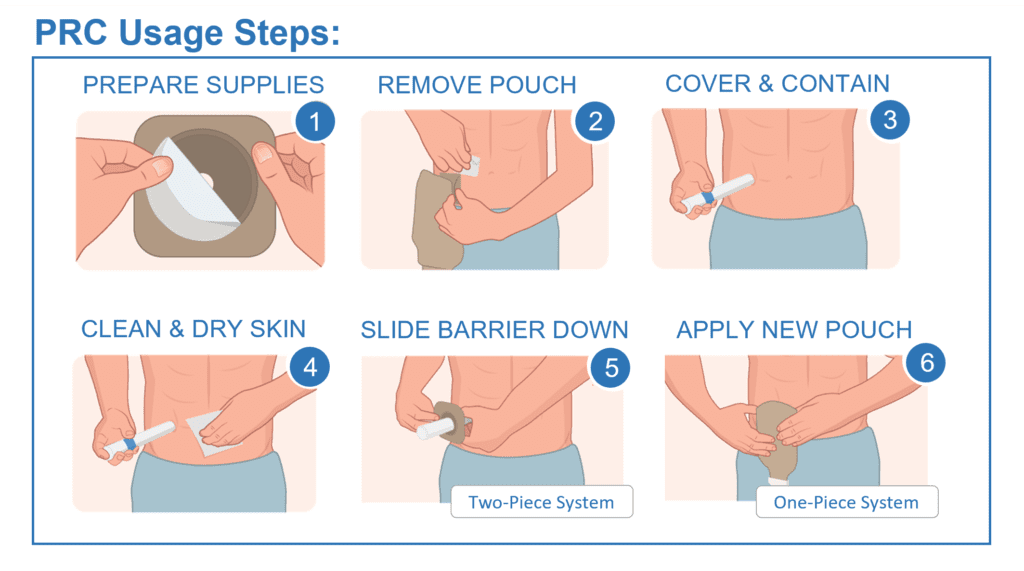
Pouch Replacement Cartridge (PRC)
The ostomy Pouch Replacement Cartridge (PRC) is a single-use, disposable cartridge used to assist with the ostomy pouching system replacement process. The PRC is placed over the stoma after the used system is removed to hygienically contain stomal output, reduce risks of effluent-to-skin contact and to allow sufficient time to clean and dry the peristomal skin during the replacement process.
Expert Review and Collaboration:
Maky Suarez, MSN, RN, WON, COCN –Mary Lou Boyer, BS Ed, RN, WOC Nurse
Joy Hooper, RN, BSN, CWOCN, OMS, WCC, WCEI®Clinical Instructor –Anita Prinz, RN, MSN, CWOCN Debi Fox, Ostomate, Ostomy Education Consultant –Reed Johnson, Editor,Illustrations, Graphic Design
Contact Us

United Ostomy Associations of America
P.O. Box 2293
Biddeford, ME 04005-2293
Call us toll-free at: 1-800-826-0826.
Our Information Line hours are Monday-Friday, 9am to 3pm EST. If you have an emergency, please dial 911 or contact your local medical professional.
Please understand that UOAA is a private, nonprofit, advocacy and informational organization. We are not a medical facility and we do not have medical or legal professionals on staff. Therefore, UOAA does not provide Medical, Mental Health, Insurance or Legal Advice. Visit UOAA Virtual Ostomy Clinic provided by The Wound Company for non-emergency, virtual ostomy support.
Get Involved
UOAA is the leading organization proactively advocating on behalf of the ostomy community. Recognizing that we are always stronger together, we encourage everyone to get involved by joining our Advocacy Network. We’ve also created several Advocacy Tools and Resources to help you successfully advocate on behalf of the ostomy community to ensure every ostomate receives quality care.